A snapshot is a form of historical backup that captures the exact state of the directory service at the time of the snapshot was taken. You can recover deleted AD items form snapshot taken by you if the Object that you want to recover was present at the time of snapshot creation.
Step 1: Creating an AD DS Snapshot
Step 2: Mount an Active Directory snapshot
Step 3: Explore a snapshot with Active Directory Users and Computers
Step 4: Unmount an Active Directory snapshot
If you encounter any error kindly drop your query in the comment box.
Step 1: Creating an AD DS Snapshot
- Open the command prompt.
- Type ntdsutil press Enter.
- Type snapshot press Enter.
- Type activate instance ntds press Enter.
- Type create press Enter.
- You should get a successful creation message with a unique GUID number for each snapshot, copy it.
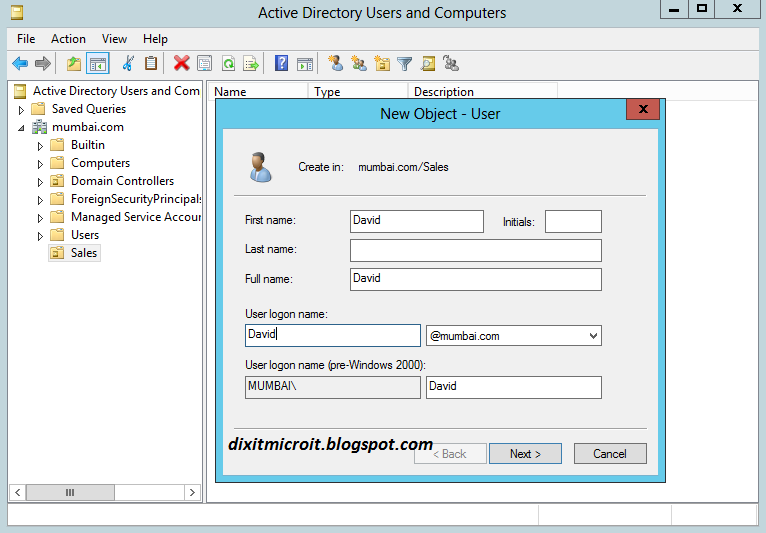
- Exit from the command prompt. And delete Dixit user that we have created in previous post from AD to test Snapshot.
Step 2: Mount an Active Directory snapshot
- Open cmd prompt as a Admin privilege type ntdsutil (a command line utility to manage AD database).
- Type snapshot then press Enter:
- Type activate instance ntds press Enter
- Type list all press Enter
- Type mount <GUID> is the GUID returned by the Create command in Step 1.
- Type quit press Enter
- Type quit press Enter
- Type the following command to add your snapshot with LDAP instance.
- Type dsamain /dbpath C:\$SNAP_datetime_volumec$\windows\ntds\ntds.dit /ldapport 44000 press Enter
Step 3: Explore a snapshot with Active Directory Users and Computers
- Switch to Active Directory Users and Computers. Right-click and then click Change Domain Controller.
- Click <Type a Directory Server name[:port] here>, type seat2.mumbai.com:44000, and then press Enter. Click OK. (replace your domain name and port number).

- Double-click mumbai.com.
- Double-click the Sales OU.
- Locate the Dixit user account object. Note that the Dixit object is displayed because the snapshot was taken prior to deleting it. Great You have done this.
- You can also unmount AD snapshot if there is no requirement for it, Follow next steps to achieve this.Open command prompt as an admin privilege and Type the following commands:
- Type ntdsutil press Enter
- Type snapshot press Enter
- Type activate instance ntds press Enter
- Type list all press Enter
- Type unmount guid (replace guid with your snapshot GUID).
- Type list all press Enter.
- Type quit and exit form cmd.
If you encounter any error kindly drop your query in the comment box.